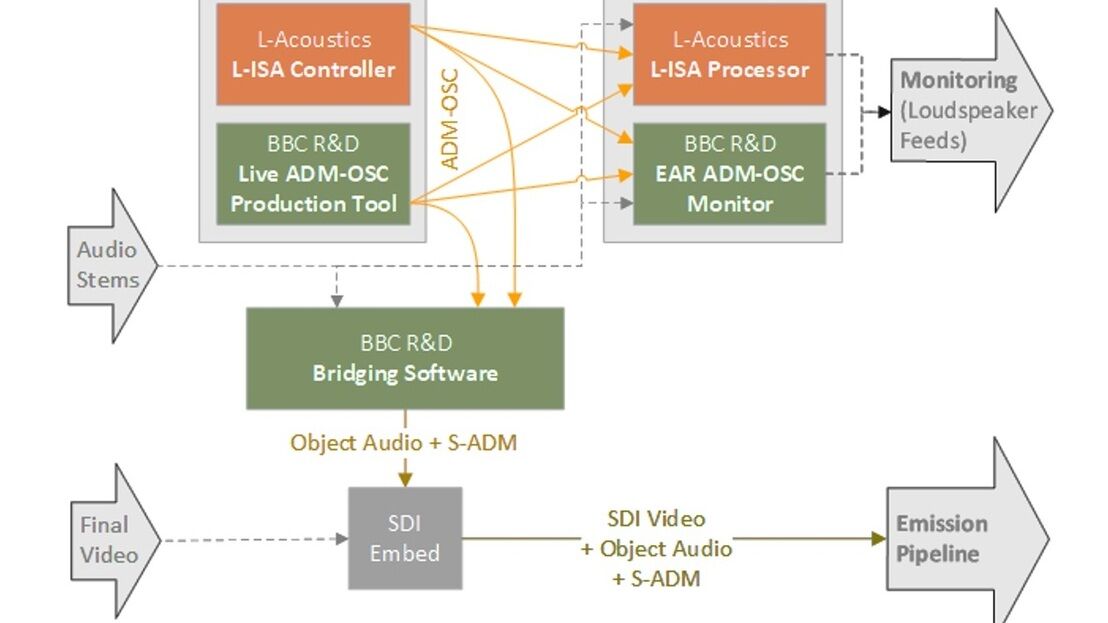
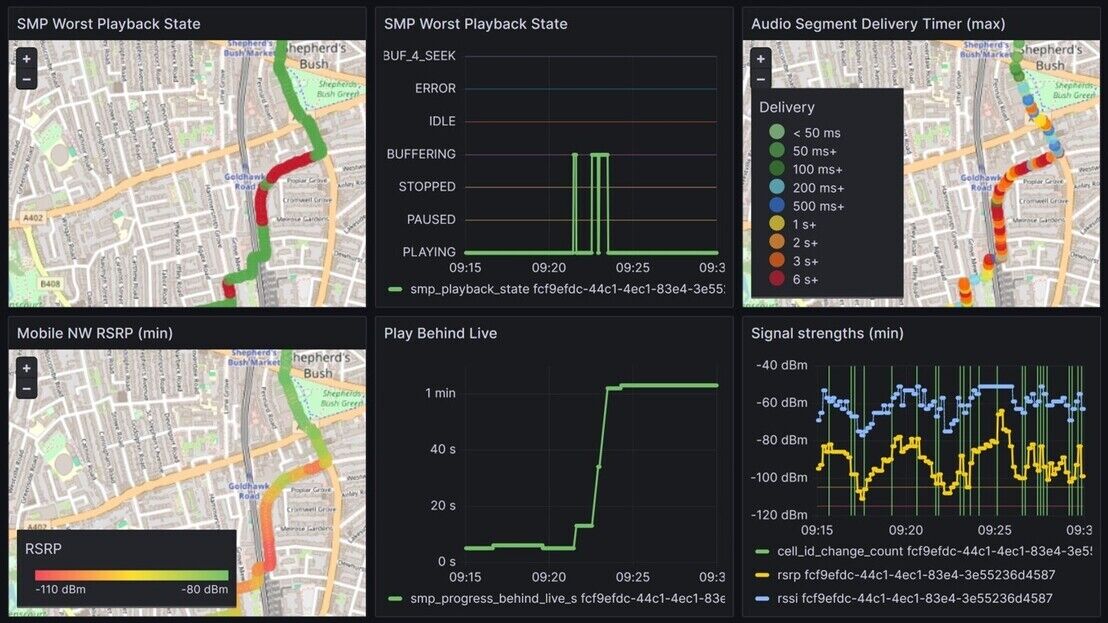
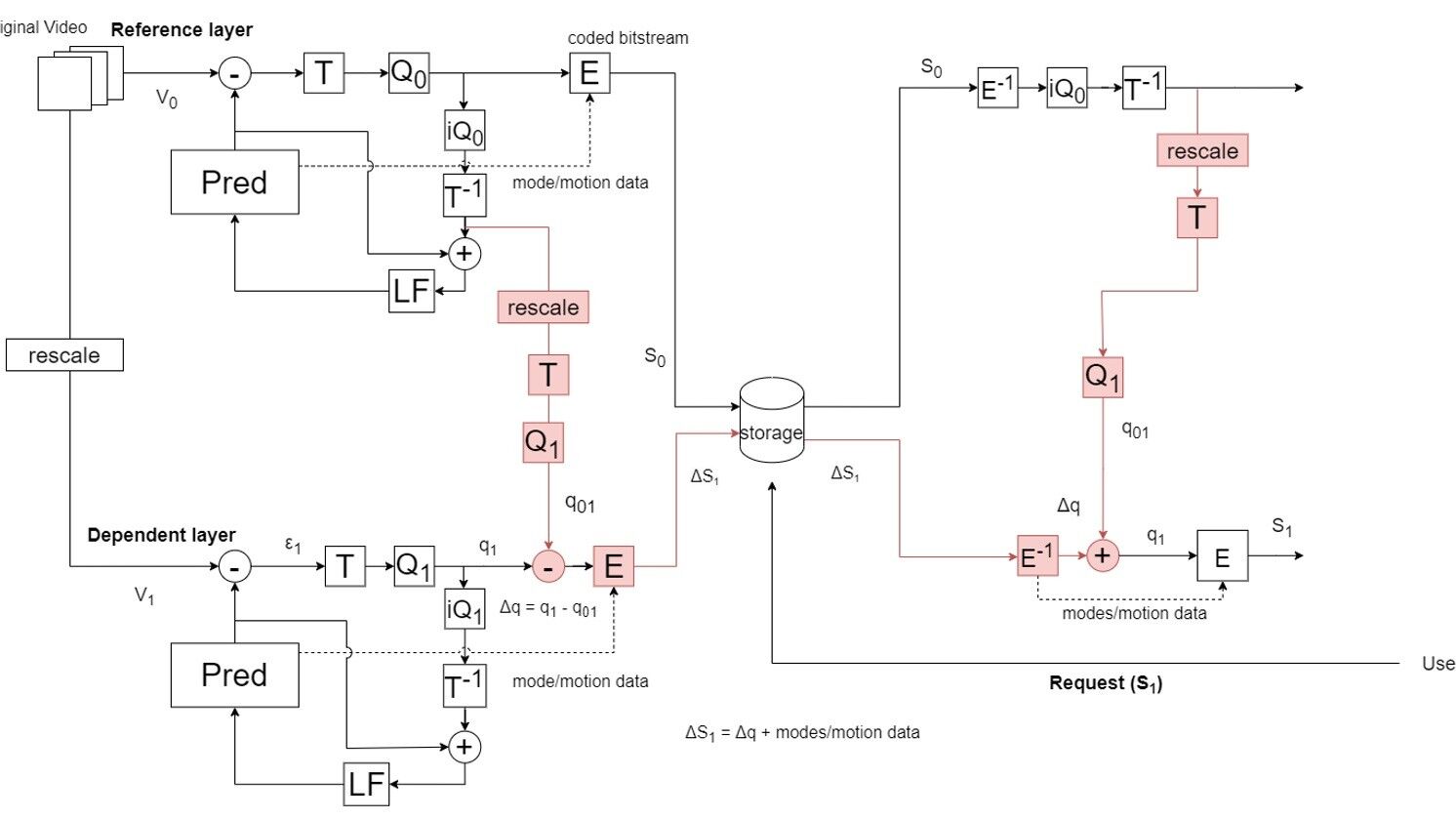
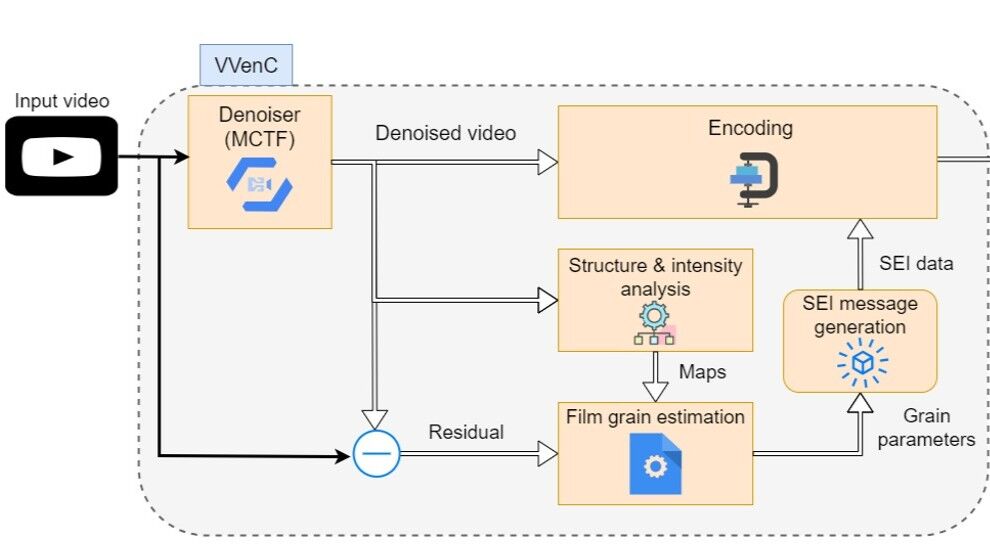
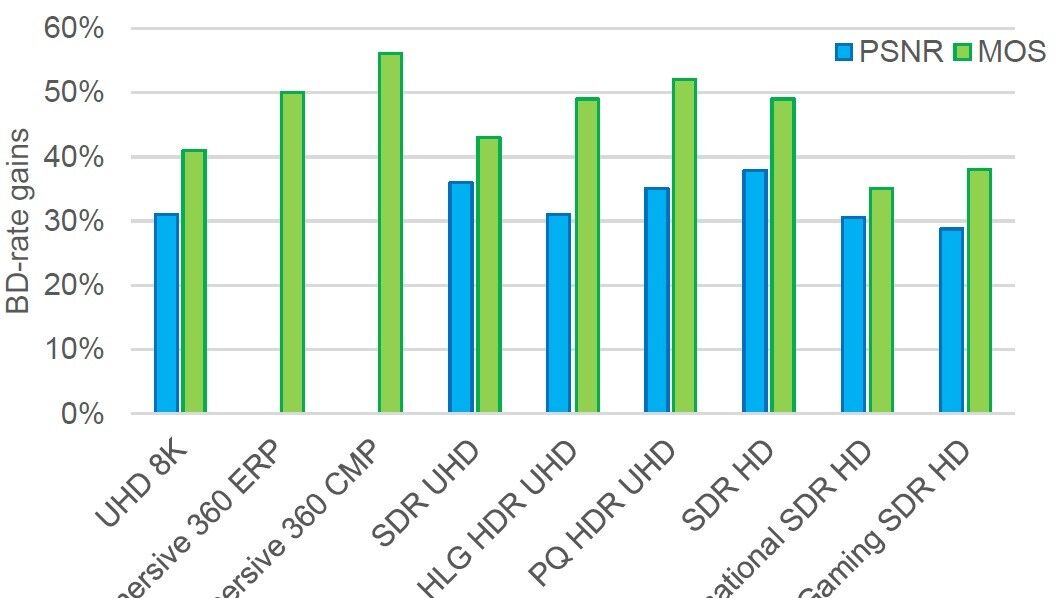
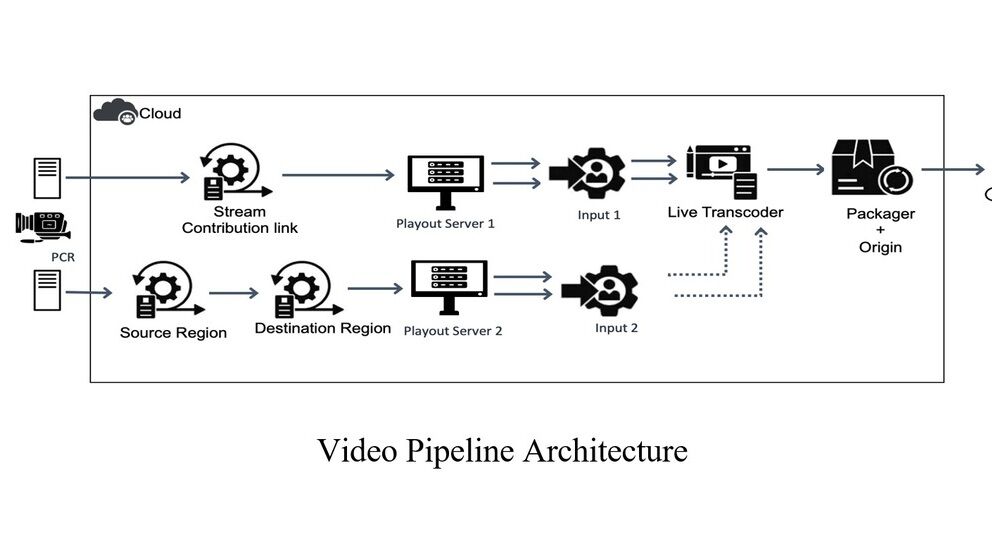
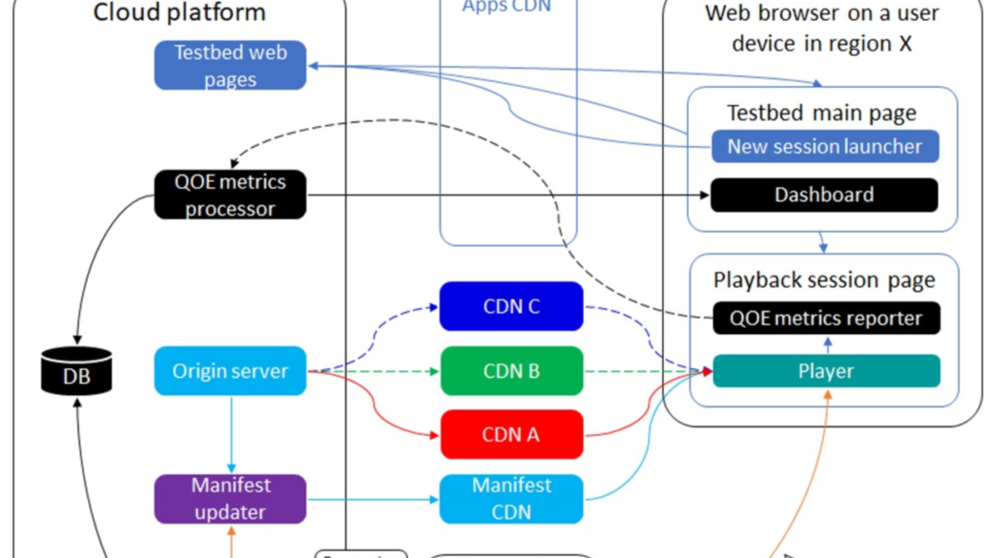
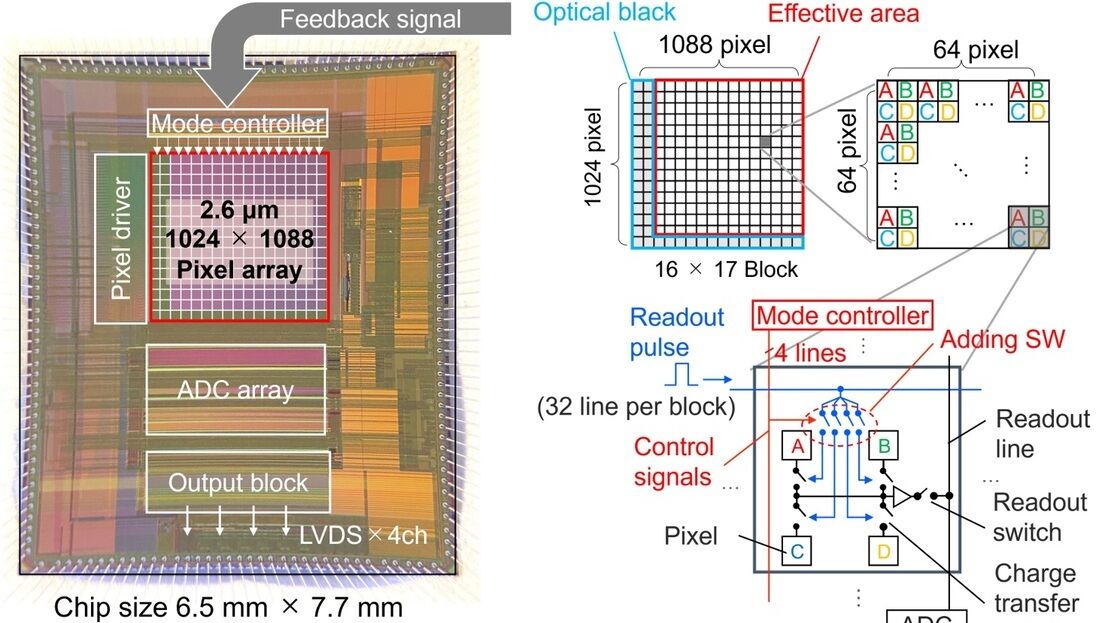
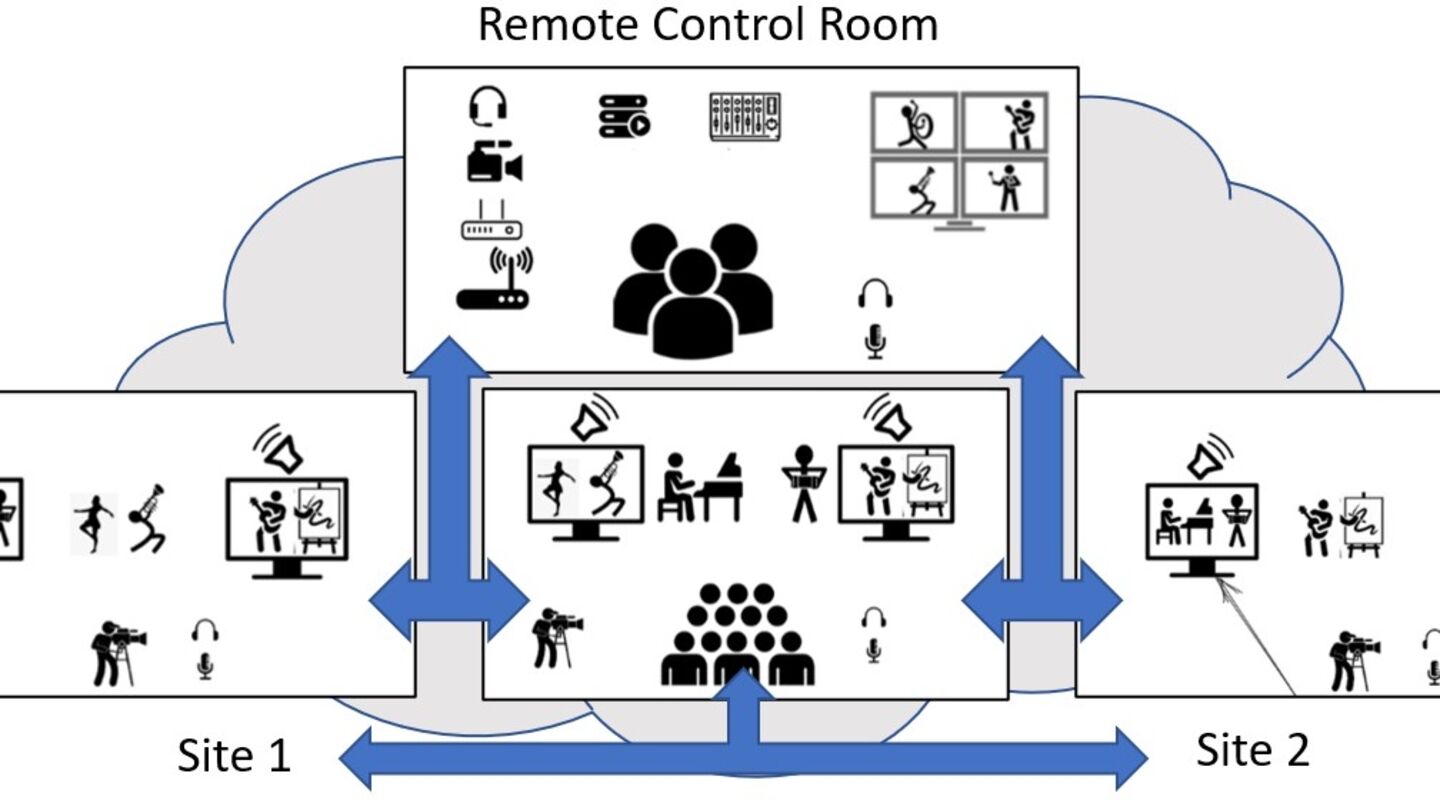
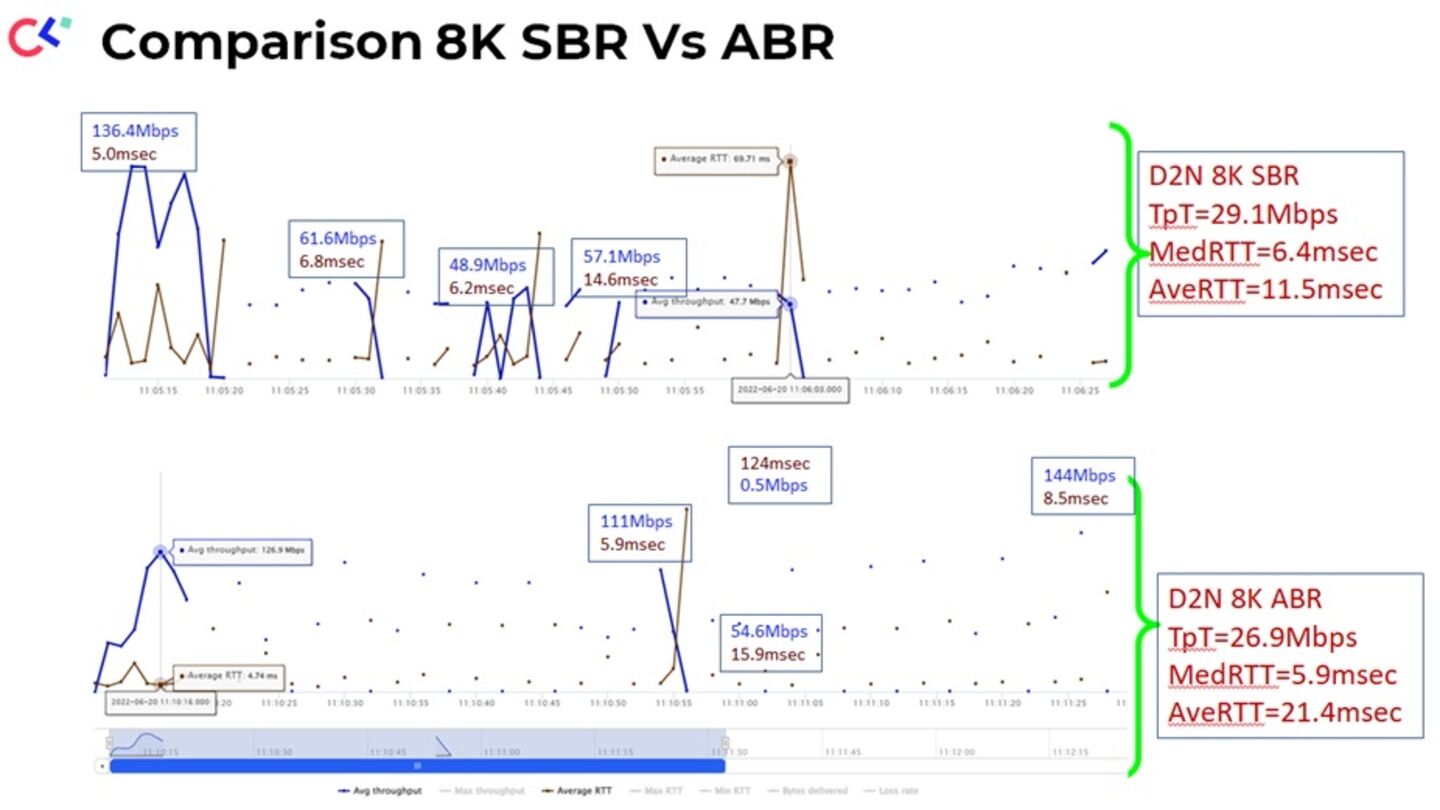
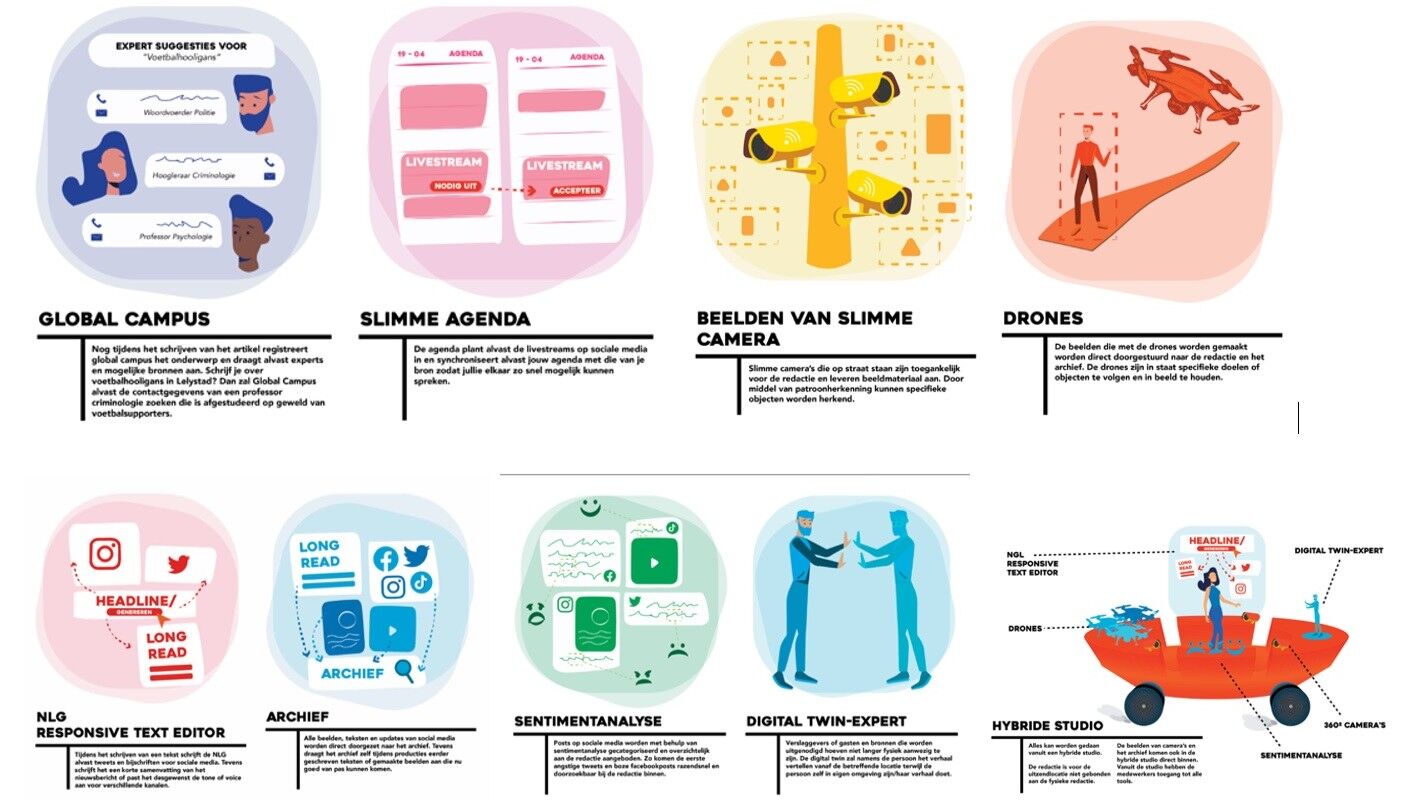
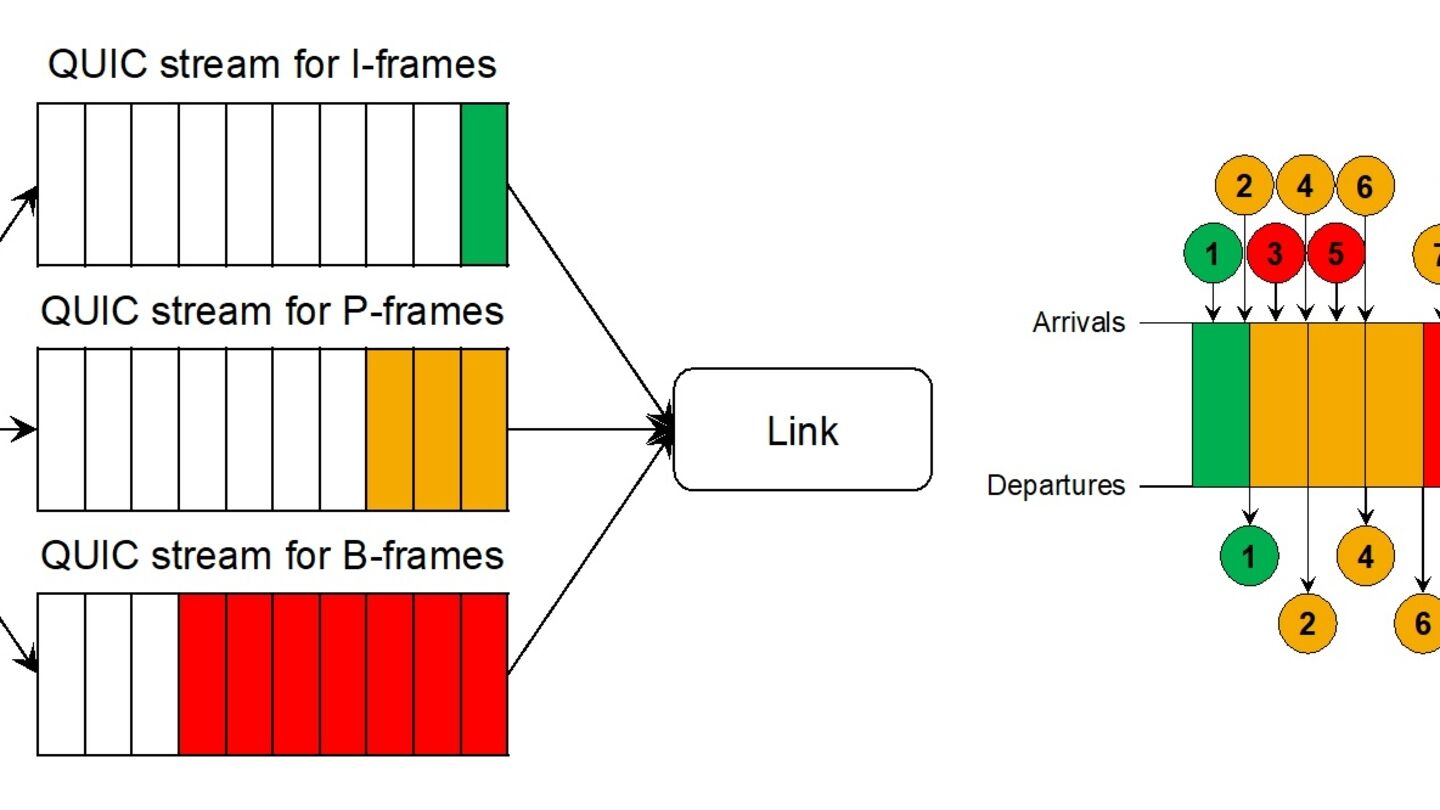
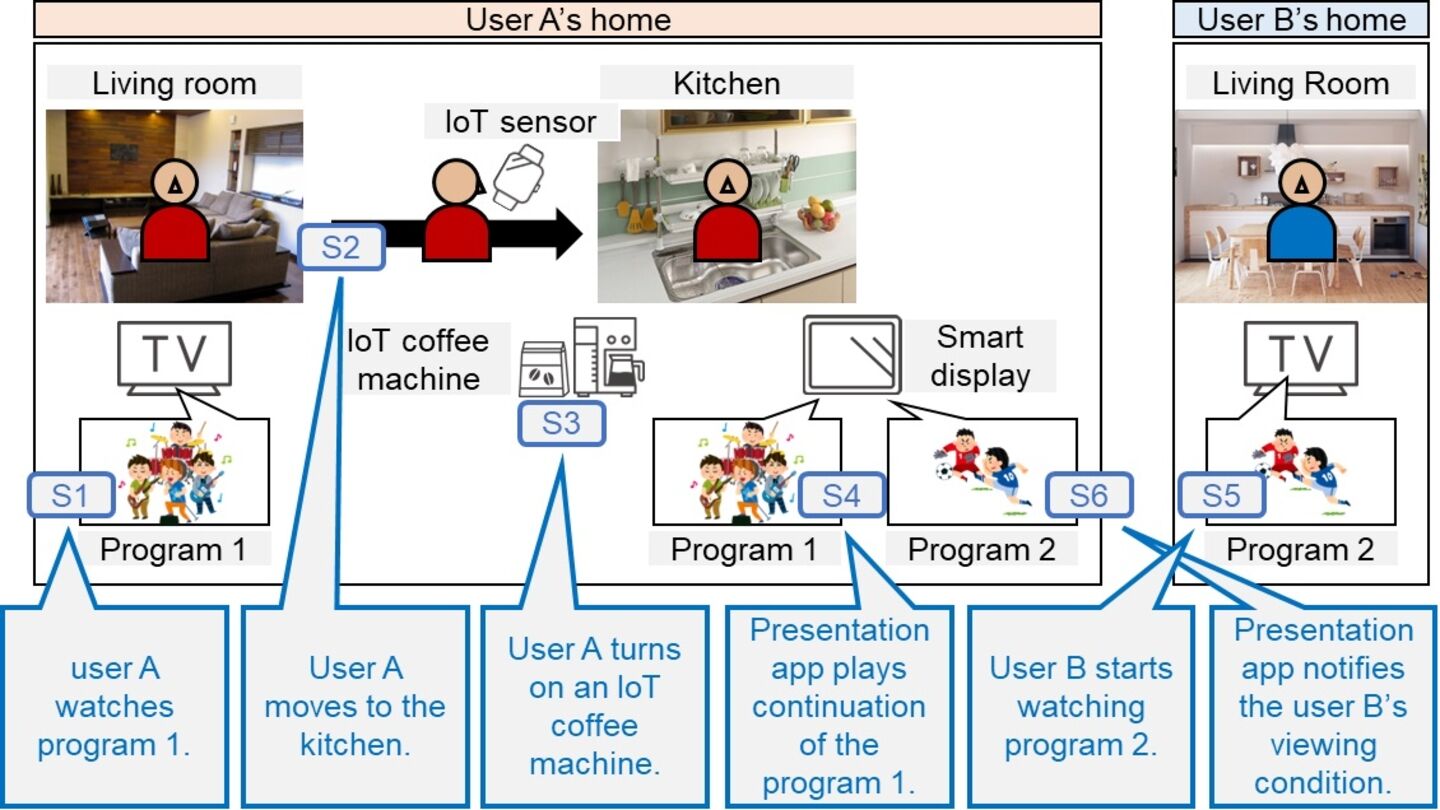
Reports

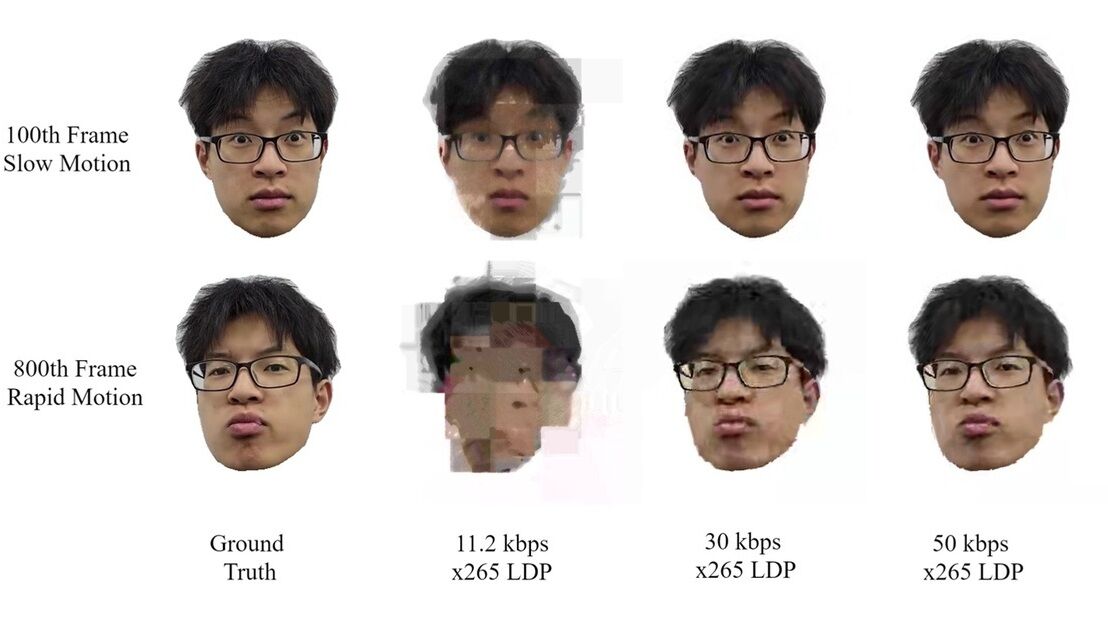
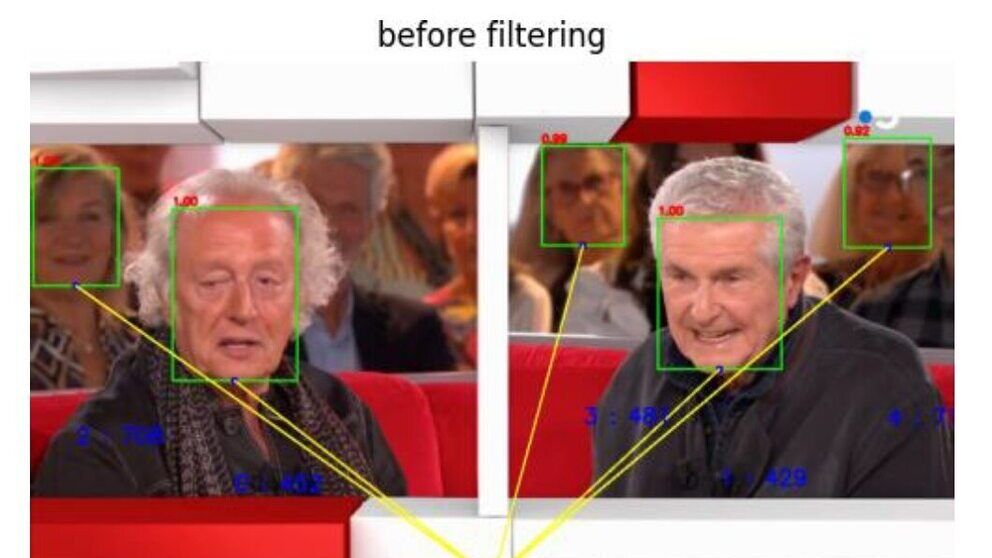
Demonstration of AI-based fancam production for the Kohaku Uta Gassen using 8K cameras and VVERTIGO post-production pipeline
Reports
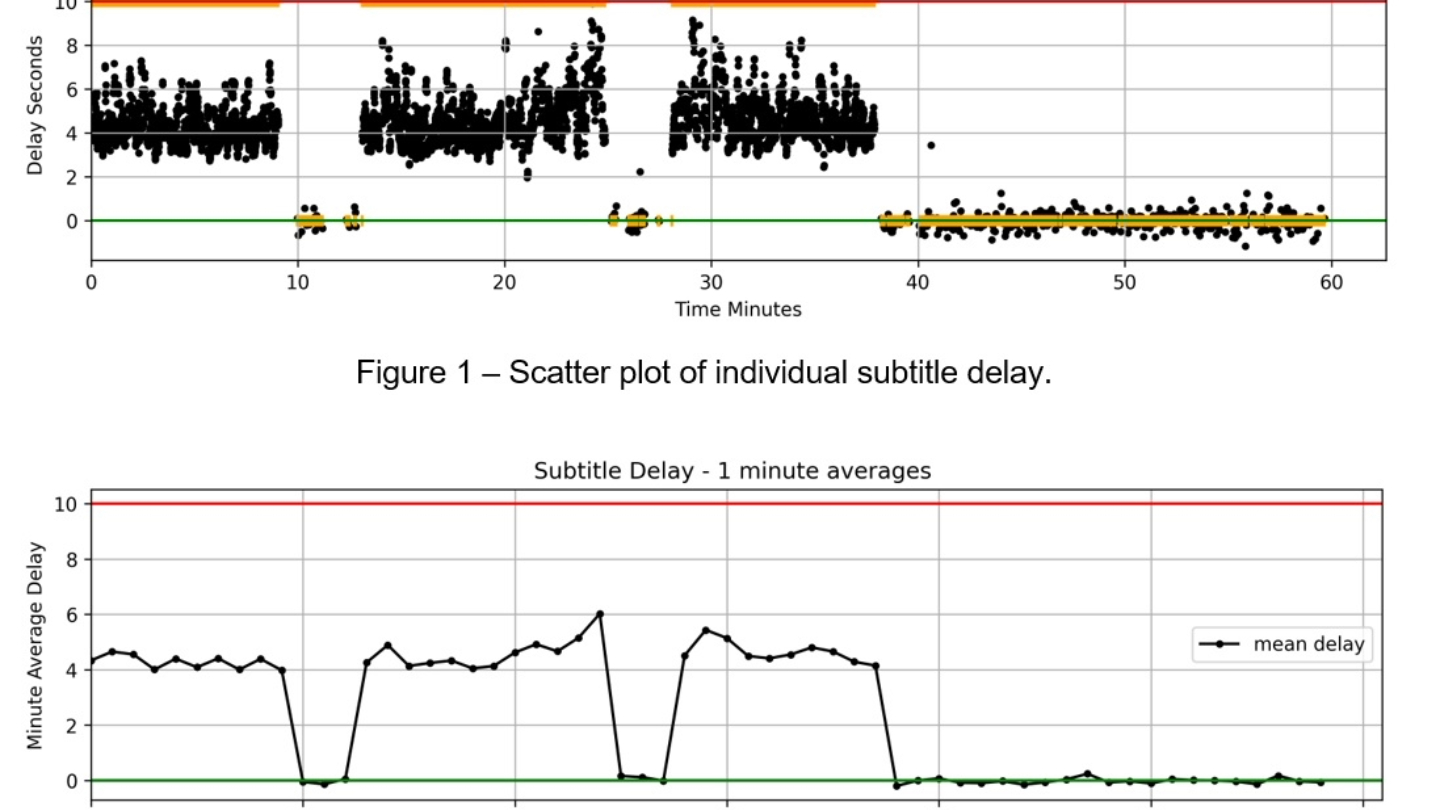
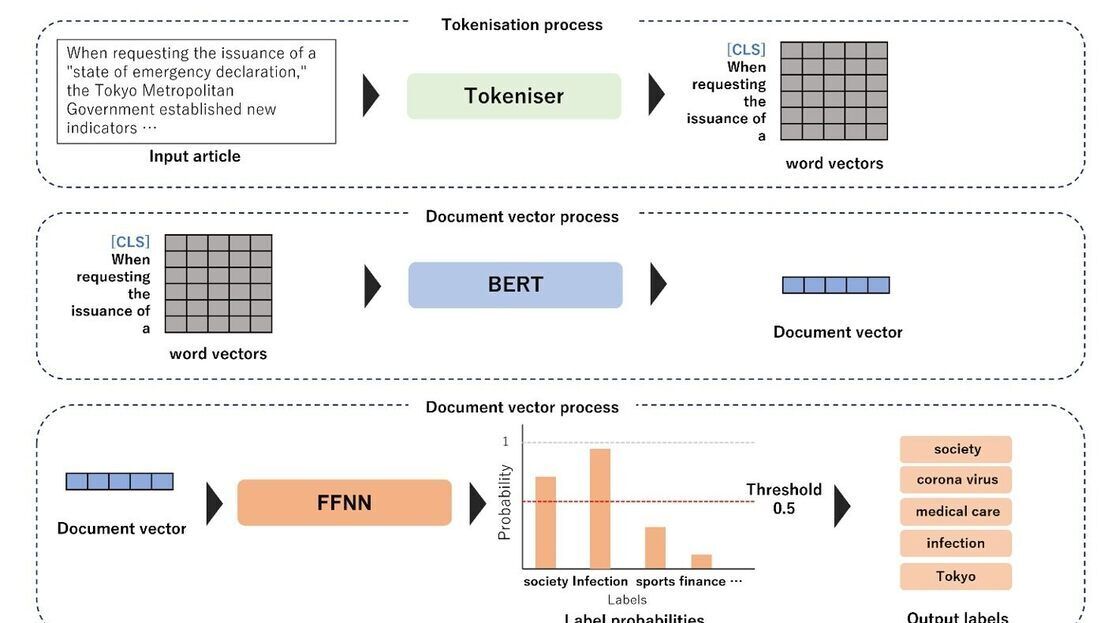
Using generative AI-speech-to-text output to provide automated monitoring of television subtitles
Reports
.jpg)
.jpg)